ANATOMY OF KIDNEY
ANATOMY OF KIDNEY
Kidney is one of the major organs of human body
It is the main organ in excretion process in our body
It's important role is to purify blood and remove unwanted waste products from our body
It is the main organ in excretion process in our body
It's important role is to purify blood and remove unwanted waste products from our body
The kidneys lie on either side of the spine in the retroperitoneal space between the parietal peritoneum and the posterior abdominal wall, well protected by muscle, fat, and ribs. They are roughly the size of your fist, and the male kidney is typically a bit larger than the female kidney.
POSITION and SIZE
The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs about 4 to 5 inches long that lie behind the abdominal cavity (between the abdominal cavity and the back muscles), one on each side of the vertebral column, slightly above the waistline.
Each kidney of the adult human weighs about 150 grams and is about the size of a clenched fist.
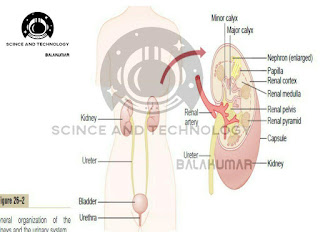
Structure
Kidney is a compound tubular gland covered by a connective tissue capsule. There is a depression on the medial border of kidney called hilum, through which renal artery, renal veins, nerves and ureter pass.
Different layers
Components of kidney are arranged in three layers
1. Outer cortex
2. Inner medulla
3. Renal sinus.
Outer cortex
Cortex is dark and granular in appearance.
It contains renal corpuscles and convoluted tubules.
At intervals, cortical tissue penetrates medulla in the form of columns, which are called renal columns or columns of Bertini.
Inner Medulla
Medulla contains tubular and vascular structures arranged in parallel radial lines.
Medullary mass is divided into 8 to 18 medullary or Malpighian pyramids.
Broad base of each pyramid is in contact with cortex and the apex projects into minor calyx.
Renal sinus
Renal sinus consists of the following structures:
i Upper expanded part of ureter called renal Pelvis
ii. Subdivisions of pelvis: 2 or 3 major calyces and about 8 minor calyces
iii. Branches of nerves, arteries and tributaries of
veins
iv. Loose connective tissues and fat.




Comments
Post a Comment